While learning any programming language, practicing the language with examples will help you to understand the concepts better. We have collected the List of Frequently asked questions (FAQ code examples) in C programming. The list contain C language basic and simple source codes and examples. Dev-C 4 Dev-C is a full-featured integrated development environment (IDE), which is able to create Windows or console-based C/C programs using the Mingw compiler system (version MSVCRT 2.95.2-1 included with this package), or the Cygwin compiler.
- Games In C++ Source Code
- Dev C Or Code Download
- Dev C++ Free Download For Windows 10
- Dev C Or Code List
- Dev C++ Code Examples
Script Hook RDR2 is released
Published on Nov 14, 2019
Script Hook RDR2 with the Native Trainer are finally released ! Have fun !
Fallout 4 Shadow Boost is released
Published on Nov 21, 2015
Users have noticed that in some locations of Fallout 4 fps gets low even with a good hardware, mostly it happens in the areas with lots of objects, Shadow Booost plugin is aimed to change that. This plugin adds an ability to dynamically control shadow draw distance depending on desired user defined fps. Make sure to test it out!
GTA V Classic Handling released
Published on May 23, 2015
GTA V features almost arcade car controls and physics, Classic Handling makes it the way it was in IV. Based on original IV handling, applies only to cars, including dlc ones. Enjoy!
Script Hook is released
Published on Apr 23, 2015
Script Hook V is released among with the Native Trainer ! Have fun with GTA V guys !
GTA V Native Database
Published on Mar 5, 2015
NATIVE DB is launched! This project is aimed to gather every piece of information about script native functions that we have, think of it as of native wiki where anyone who wants to contribute can do so and everyone who needs the latest script documentation or the header with natives for ScriptHook can get it right there!
CLEO update
Published on Dec 5, 2014
Update for CLEO is here! Cooking recipes free download. Latest version of GTA San Andreas is fully supported now, library compatibility is improved! Also GTA San Andreas cheats script supports 3gb RAM devices now.
GTA V Script and Native Research
Published on Jun 22, 2014
Today our research on GTA V scripts and natives goes public, it includes decompiled scripts, natives and every other thing you need to know in order to start making script mods when PC version arrives. Research is available in this gtaforums topic.
openFormats I/O update
Published on Apr 18, 2014
openFormats I/O finally got the support of GTA IV fragments (*.oft), new version also comes with fixed tangents support.
- C++ Basics
- C++ Object Oriented
- C++ Advanced
- C++ Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
When we consider a C++ program, it can be defined as a collection of objects that communicate via invoking each other's methods. Let us now briefly look into what a class, object, methods, and instant variables mean.
Object − Objects have states and behaviors. Example: A dog has states - color, name, breed as well as behaviors - wagging, barking, eating. An object is an instance of a class.
Class − A class can be defined as a template/blueprint that describes the behaviors/states that object of its type support.
Methods − A method is basically a behavior. A class can contain many methods. It is in methods where the logics are written, data is manipulated and all the actions are executed.
Instance Variables − Each object has its unique set of instance variables. An object's state is created by the values assigned to these instance variables.
C++ Program Structure
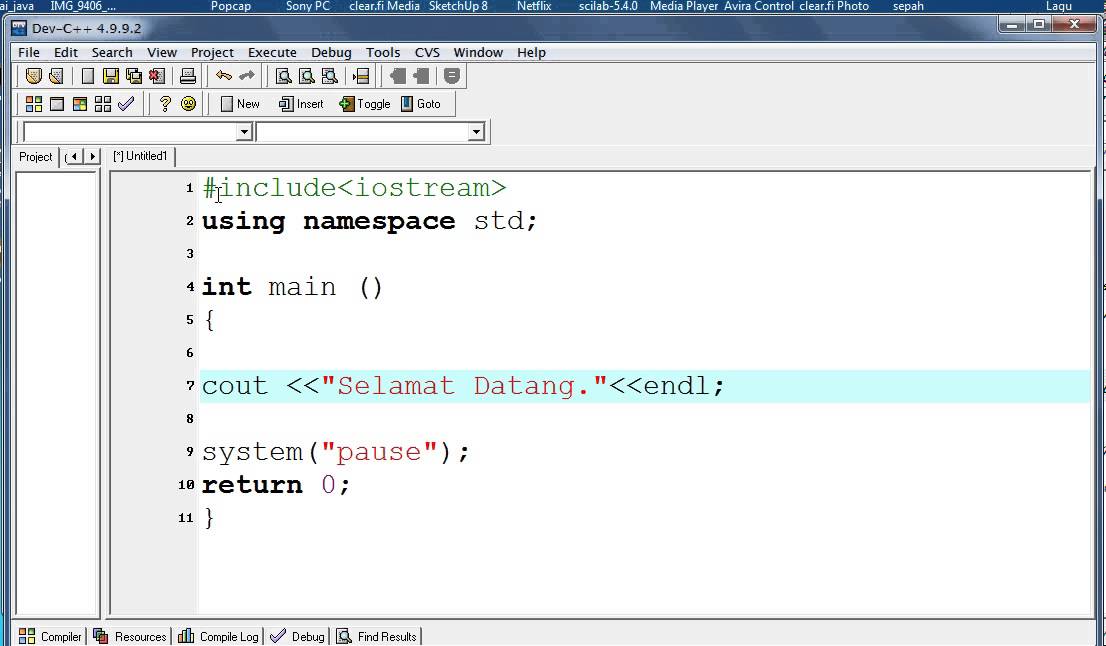
Let us look at a simple code that would print the words Hello World.
Let us look at the various parts of the above program −
The C++ language defines several headers, which contain information that is either necessary or useful to your program. For this program, the header <iostream> is needed.
The line using namespace std; tells the compiler to use the std namespace. Namespaces are a relatively recent addition to C++.
The next line '// main() is where program execution begins.' is a single-line comment available in C++. Single-line comments begin with // and stop at the end of the line.
The line int main() is the main function where program execution begins.
The next line cout << 'Hello World'; causes the message 'Hello World' to be displayed on the screen.
The next line return 0; terminates main( )function and causes it to return the value 0 to the calling process.

Compile and Execute C++ Program
Let's look at how to save the file, compile and run the program. Please follow the steps given below −
Open a text editor and add the code as above.
Save the file as: hello.cpp
Open a command prompt and go to the directory where you saved the file.
Type 'g++ hello.cpp' and press enter to compile your code. If there are no errors in your code the command prompt will take you to the next line and would generate a.out executable file.
Now, type 'a.out' to run your program.
You will be able to see ' Hello World ' printed on the window.
Make sure that g++ is in your path and that you are running it in the directory containing file hello.cpp.
You can compile C/C++ programs using makefile. For more details, you can check our 'Makefile Tutorial'.
Semicolons and Blocks in C++
In C++, the semicolon is a statement terminator. That is, each individual statement must be ended with a semicolon. It indicates the end of one logical entity.
For example, following are three different statements −
A block is a set of logically connected statements that are surrounded by opening and closing braces. For example −
C++ does not recognize the end of the line as a terminator. For this reason, it does not matter where you put a statement in a line. For example −
Games In C++ Source Code
is the same as
C++ Identifiers
A C++ identifier is a name used to identify a variable, function, class, module, or any other user-defined item. An identifier starts with a letter A to Z or a to z or an underscore (_) followed by zero or more letters, underscores, and digits (0 to 9).
C++ does not allow punctuation characters such as @, $, and % within identifiers. C++ is a case-sensitive programming language. Thus, Manpower and manpower are two different identifiers in C++.
Here are some examples of acceptable identifiers −
C++ Keywords
Dev C Or Code Download
The following list shows the reserved words in C++. These reserved words may not be used as constant or variable or any other identifier names.
Dev C++ Free Download For Windows 10
| asm | else | new | this |
| auto | enum | operator | throw |
| bool | explicit | private | true |
| break | export | protected | try |
| case | extern | public | typedef |
| catch | false | register | typeid |
| char | float | reinterpret_cast | typename |
| class | for | return | union |
| const | friend | short | unsigned |
| const_cast | goto | signed | using |
| continue | if | sizeof | virtual |
| default | inline | static | void |
| delete | int | static_cast | volatile |
| do | long | struct | wchar_t |
| double | mutable | switch | while |
| dynamic_cast | namespace | template |
Trigraphs
A few characters have an alternative representation, called a trigraph sequence. A trigraph is a three-character sequence that represents a single character and the sequence always starts with two question marks.
Trigraphs are expanded anywhere they appear, including within string literals and character literals, in comments, and in preprocessor directives.
Following are most frequently used trigraph sequences −
| Trigraph | Replacement |
|---|---|
| ??= | # |
| ??/ | |
| ??' | ^ |
| ??( | [ |
| ??) | ] |
| ??! | |
| ??< | { |
| ??> | } |
| ??- | ~ |
All the compilers do not support trigraphs and they are not advised to be used because of their confusing nature.
Whitespace in C++
A line containing only whitespace, possibly with a comment, is known as a blank line, and C++ compiler totally ignores it.
Whitespace is the term used in C++ to describe blanks, tabs, newline characters and comments. Whitespace separates one part of a statement from another and enables the compiler to identify where one element in a statement, such as int, ends and the next element begins.
Statement 1
Applied linguistics guy cook pdf download. In the above statement there must be at least one whitespace character (usually a space) between int and age for the compiler to be able to distinguish them.
Dev C Or Code List
Statement 2
Dev C++ Code Examples
In the above statement 2, no whitespace characters are necessary between fruit and =, or between = and apples, although you are free to include some if you wish for readability purpose.